Portable welding fume extractors or mobile welding fume extractors are the compact yet movable fume extraction systems which can be used to capture fumes at source capture method, here we discuss, ESP- Based Portable welding fume extractors: Compact clean air solutions to effectively capture fumes and dirt in the workplace with Filter ON India’s 43 years expertise in clean air solutions sector.
Portable Welding Fume Extractors: What it is?
When there is welding required for a big job that is handled by crane, we can’t use suction hoods there, so in that condition, the Portable Fumes Extractor plays a very important role in removing fumes and dirt from that area.
In the Portable Fumes Extractor, there is a self-standing suction arm that the welder can adjust whenever they required. To suck fumes from welding, the suction hood should be placed 100–300 mm near the welding work, as shown in Image A.
Filter ON Fumes Extractor Image B, where a blower (fan) and a filter are used, which suck the fumes and filter them.
Why is the Portable Welding Fume Extractors the best choice?
A Portable welding fume extractor is best choice in following situation:
- It is the best choice when there are large welding jobs i.e. earthmover buckets welding, propeller shafts welding in shipyards is in operation.
- It is the best choice where canopy hood structure is not applicable.
- It is the best choice when there is a welding operation carried in different parts of the work area and fumes are spread everywhere so a moving type fume extraction system is required.
- It is the best choice when you want to use fume extraction simultaneously as and when required this can be achieved by a self standing suction arm as shown in the above image.
Selection of Portable Welding Fume Extractors:
Selection of portable welding fume extractor is a strategic and commercial decision for anyone as it will benefits in –
Compact and Portable in nature:
Portable fume extractor as their name implies compact and portable in nature it can accommodate in very low space as well and as their moving ability you can easily use them anywhere in the work area.
No Filter Replacement Needed:
These Portable Fume Extractors are equipped with electrostatic precipitation technology, a technology that is very useful in long term structure. Here you need to maintain a periodic cleaning cycle of the filters and esp stacks to remove dirt and dust which improves efficiency and performance.
Versatility:
Portable fume extractors versatile nature can be used as the operations changes they are used at source capture at various fume pointers around the work area using the portable wheels and self suction arms.
The selection of portable fume extractor is based on what is the application? I.e. welding type, space in the work area, operational frequency, requirement of size of system i.e. CFM capacity etc. On the basis of these factors the selection should be made.
Factors That Influence the Selection of Portable Fume Extractors
Choice of Technology:
Electrostatic Precipitation (ESP) technology is used, as it is more flexible and cost-effective compared to other filtration technologies. Leading industrial filtration manufacturers like Filter ON India have been providing solutions based on ESP technology for over 40+ years, making it a proven and reliable choice.
Power Consumption:
Portable fume extractors based on ESP technology consume approximately 50% less power than cartridge or media filter–based solutions. This significantly improves productivity while operating under limited power availability.
Suction Capacity:
The suction capacity of ESP-based portable fume extraction systems is superior compared to other technologies such as cartridge filters. In cartridge systems, filters gradually get filled with dust and fumes, which hampers overall suction performance. This issue does not arise in ESP systems, as the gaps between plates are high (7-8mm) which allows easy passage of air even in loaded condition without hampering the suction capacity.
Efficiency in Operation:
The operational efficiency of portable welding fume extractors is maintained through washable filters that can be used for a long duration. Dirt and contaminants are removed using a special type of chemical cleaning process, restoring the filters to near-new condition and ensuring sustained high efficiency.
Longevity:
ESP-based portable fume extractors offer longer service life due to their robust built-in methodology, including the construction materials used for ESP stacks, filters, and related components. These stacks and filters are reusable in nature, and periodic cleaning helps maintain efficiency and ensures long-term reliable performance.
Compliance Friendly:
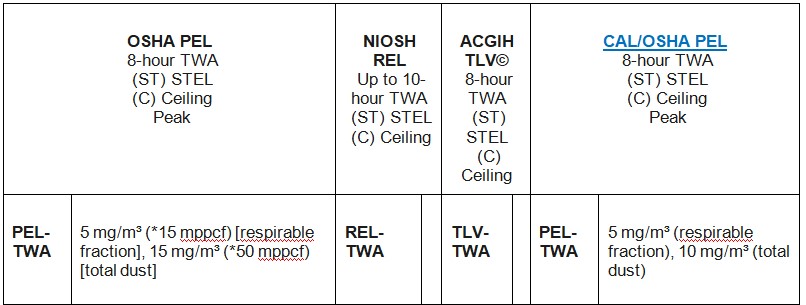
ESP-based portable fume extraction systems are compliance-friendly and adhere to CPCB, OSHA, and EPA standards. These systems are equally compliance-ready when compared to other cartridge-based filtration systems.
Low Cost:
The long-term cost of ESP-based portable fume extractors is lower due to minimal maintenance requirements. Since the filters and stacks are washable and reusable, replacement costs are significantly reduced, making the system economical over an extended period of use.
Some of the installation images of ESP-Based Portable Welding Fume Extractors:
Key Industries & Applications:
There are various key industries and applications where Portable Fume Extractors may have used they are as follows:
- Welding & Metalworking: Portable Fume Extractors effectively captures fumes from welding types such as MIG, TIG, arc welding, plasma cutting, grinding, and general dust.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Portable fume extractors are essential for soldering, removing harmful fumes from components.
- Vehicle Services (Auto Body Shops): Portable fume extractors are ideal for light to medium welding and repair tasks.
- Woodworking: It Removes sawdust and particles from sanding and cutting.
- Laboratories & Pharmaceuticals: ESP Based Portable fume extractros are great choice for handling specific chemical fumes, soldering, or small experiments.
- 3D Printing & Composite Machining: It captures fumes and particles during material processing operations.
So the portable fume extractors are a great choice in the above industries and applications and especially if they are equipped with Filter ON ESP’s then it will be greatly effective for efficiency and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
F 1: What is an ESP-based portable welding fume extractor?
An ESP-based portable welding fume extractor uses electrostatic precipitation technology to capture welding fumes, smoke, and fine particulate matter. It charges airborne contaminants electrically and collects them on washable ESP plates, ensuring efficient filtration with low pressure drop.
F 2: Why are ESP-based portable welding fume extractors more energy-efficient?
ESP-based portable welding fume extractors consume up to 50% less power compared to cartridge or media filter systems. Since there is no filter clogging, airflow remains stable, reducing fan load and overall energy consumption.
F 3: How do washable filters improve performance in ESP-based systems?
Washable ESP filters can be cleaned using a special chemical cleaning process, restoring them to near-original condition. This prevents suction loss, maintains consistent filtration efficiency, and eliminates frequent filter replacement costs.
F 4: Are ESP-based portable welding fume extractors compliance-friendly?
Yes, ESP-based portable welding fume extractors are designed to meet CPCB, OSHA, and EPA standards. They effectively control welding fumes and particulate emissions, making them suitable for compliance-focused industrial environments.