Navigating the Challenges of High-Speed 5-Axis CNC Grinding: A Focus on Oil Mist Management
Oil mist collectors are a critical consideration for CNC 5-axis grinding machine and tool/cutter grinder operations. As the business landscape evolves, the application of 5-axis grinding machines is also changing, necessitating the implementation of effective oil mist collection solutions. Modern CNC facilities increasingly prioritize oil mist management to control coolant mist, minimize maintenance issues, and maintain a cleaner production environment. We need to proactively address the hazardous fumes and mists produced in 5-axis grinding to ensure worker productivity and overall workplace air quality. This blog post will explore Oil Mist Collector solutions for 5-axis grinding machines and their benefits for improving workplace productivity.
Oil Mist Challenges in 5- Axis Grinding

5-axis grinding presents significant challenges related to oil mist, including:
- Health Challenges:
- Machine & Safety Challenges
- Operational Challenges
- Compliance Challenges
Health Challenges:
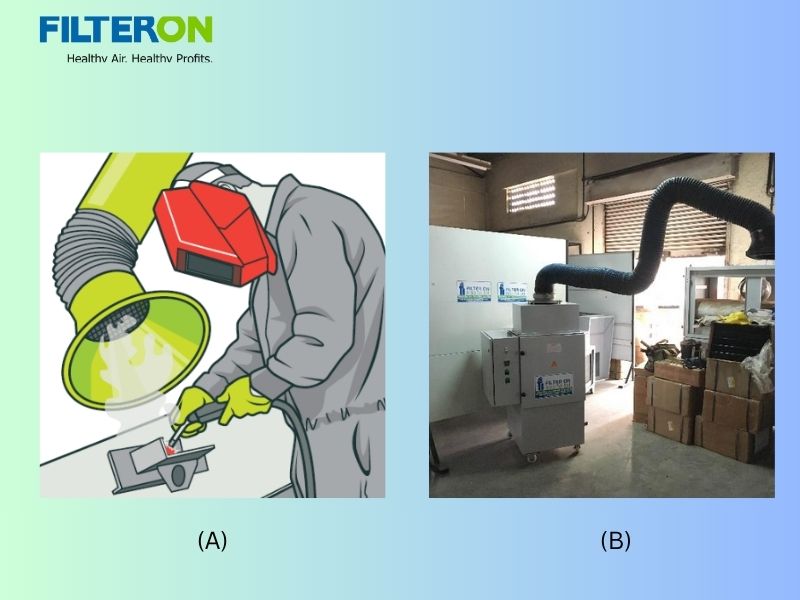
High-speed operations generate microscopic mist and smoke, which can lead to airborne oil droplets that, upon inhalation, can trigger respiratory problems, irritation, and dermatitis.
Machine & Safety Challenges:
Oil mist can compromise sensitive CNC machine components, such as electronic controls, sensors, and slides, causing premature failure and increasing maintenance costs.
Potential for slip and fall hazards, fire hazards, and reduced visibility due to escaped oil mist settles on floors, walls, and other surfaces, creating slippery conditions and increasing injury risk. Settled oil residue can form flammable lines or layers on surfaces, presenting a potential fire risk in the workshop. Effective oil mist management is essential in high-speed 5-axis grinding environments to maintain safe air quality and protect machine operators from prolonged exposure to hazardous aerosols.
Operational Challenges:
Potential for slip and fall hazards, fire hazards, and reduced visibility due to escaped oil mist settles on floors, walls, and other surfaces, creating slippery conditions and increasing injury risk. Settled oil residue can form flammable lines or layers on surfaces, presenting a potential fire risk in the workshop.
Compliance Challenges:
Regulatory bodies like OSHA in the US stipulate maximum exposure limits (e.g., 5 mg/m³) for mineral oil mist, requiring employers to implement robust control measures. Investing in proper oil mist management systems not only enhances workplace safety but also helps organizations meet regulatory air-quality standards and sustain efficient operations.
Solutions for overcoming challenges:
Filter ON India specializes in designing and implementing sophisticated Oil Mist Collector solutions for 5-axis grinding. Our team of experienced engineers leverages decades of expertise in electrostatic precipitators to deliver optimized air quality, minimize maintenance costs, and ensure full compliance. We’ve established strong rapport with our collaborators to providing a wide array of highly efficient and effective oil mist collectors like ESP-based solutions. Know more about our solutions.
How Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) Oil Mist Collectors Improve Air Quality in 5-Axis CNC Machining
5-axis CNC machines are known for their speed, precision, and ability to perform complex operations such as grinding, gear cutting, and tapping. However, these advantages come with a serious downside: heavy oil mist, smoke, and coolant vapor in the air. Without proper air filtration, this airborne contamination can affect machine performance, worker health, and shop safety.
This is where Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) oil mist collectors make a major difference. By using high-voltage electrostatic technology, ESP systems capture ultra-fine oil particles that traditional filters struggle to remove, helping manufacturers maintain a cleaner, safer, and more efficient workspace.
1. Capturing Ultra-Fine Oil Mist That Standard Filters Miss
The Challenge:
High-speed 5-axis machining uses neat oils and high-pressure coolant systems that generate microscopic mist and smoke. These particles are often so small that conventional mechanical filters allow them to pass through.
The ESP Advantage:
ESP collectors remove extremely fine particles by electrically charging them and pulling them out of the airflow. As contaminated air passes through the system, mist particles receive an electrical charge and are then attracted to collection plates. This process allows the system to capture even sub-micron oil particles, dramatically improving air quality around the machine.
2. Designed for Sticky Oils and Heavy Mist Loads
The Challenge:
Operations like 5-axis grinding and gear cutting often rely on thick, high-viscosity oils. These sticky contaminants quickly clog conventional filter media, causing airflow restriction and frequent shutdowns for maintenance.
The ESP Advantage:
ESP collectors do not rely on disposable filter media. Instead, oil mist collects on solid metal plates and drains away. This design prevents clogging, maintains consistent airflow, and allows the system to perform reliably even in high-load, oil-heavy machining environments.
3. Lower Operating Costs with Washable Collection Cells
The Challenge:
Replacing HEPA or mechanical filters in high-production CNC shops adds up costs quickly. Filter replacement costs, downtime, and disposal fees can become a long-term operational burden.
The ESP Advantage:
ESP oil mist collectors use reusable, washable collection cells. These components can be cleaned and put back into service for years, significantly reducing replacement costs. This approach lowers operating expenses and supports sustainability goals by cutting down on waste.
4. Low Running Cost for 5-Axis CNC Machine Mist Filtration
The Challenge
5-axis CNC machines operate continuously and consume significant electrical power due to simultaneous multi-axis motion, high spindle speeds, and coolant systems as well as Mist Collector.
When conventional media-type filtration systems are used for oil mist extraction, they introduce:
- Higher static pressure drop
- Increased blower power consumption
- Frequent filter replacement costs
- Production downtime during maintenance
This results in additional operational expenditure (OPEX), increasing the total cost of ownership for manufacturers.
The ESP Advantage
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)-type mist collectors offer a more energy-efficient and cost-effective alternative.
Key advantages include:
- Reusable, washable collection cells – No recurring filter media replacement cost
- Low pressure drop – Reduced fan/blower energy requirement
- Stable airflow performance – Even under high mist load conditions
- Lower overall power consumption – Typically up to 40–50% lower compared to conventional media filtration systems (application-dependent)
This significantly reduces long-term operating costs while maintaining high filtration efficiency.
5. Better Operator Safety and Oil Recovery
The Challenge:
Airborne oil mist contributes to respiratory problems, skin irritation, and slippery floors. Over time, poor air quality can lead to health issues, compliance risks, and unsafe working conditions.
The ESP Advantage:
By removing fine oil particles from the air, ESP systems help create a healthier shop environment. The captured oil drains into a collection tray, where it can often be recycled or properly disposed of. This improves housekeeping, reduces waste, and supports environmental compliance.
Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) oil mist collectors are a practical long-term solution for the air quality challenges created by high-speed 5-axis CNC machining. They deliver superior fine-particle capture, resist clogging from sticky oils, reduce maintenance costs with washable components, fit easily into tight machine layouts, and contribute to safer, cleaner work environments.
For manufacturers running 5-axis CNC equipment, investing in an ESP mist collection system is not just about compliance; it’s about protecting workers, extending equipment life, and maintaining a professional, high-performance machining operation.
By implementing advanced oil mist management solutions, manufacturers can significantly reduce airborne contaminants while improving machine reliability and overall shop floor productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the primary benefits of using an Oil Mist Collector for 5-axis CNC grinding machines?
Oil mist collectors significantly reduce the hazards associated with high-speed machining, including inhalation of harmful particulate matter. They address concerns around worker health, ensure safe operational conditions, and minimize potential regulatory non-compliance.
How does an Oil Mist Collector improve air quality compared to traditional filtration methods?
Unlike conventional filters, ESP collectors capture microscopic oil particles that traditional systems miss. This results in a vastly cleaner and more efficient workspace, reducing the risk of respiratory issues, skin irritation, and improved visibility.
What types of challenges can 5-axis grinding machines face regarding oil mist?
5-axis grinding machines are prone to viscous oils, causing clogging issues with standard media filters. Electrostatic Oil mist collectors prevent this, maintaining consistent airflow, and ensuring the system’s reliability.
What makes Filter ON India's ESP oil mist collectors unique and effective?
We differentiate ourselves through a combination of proven technologies including electrostatic precipitators optimized for the unique demands of 5-axis machining. Our systems are designed for low maintenance, and are easily integrated into existing equipment, ensuring a seamless and efficient solution.