Clearing the Air: Understanding Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) – Examining Pollution, Health Impacts, Safety Limits, and Industrial Solutions for Risk Mitigation
When we think about pollution, we have thoughts about its various sources and main pollutants, such as transportation, industrial pollution, CO2, SO2, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). VOCs are small organic compounds that are present in the air and play a vital part in air pollution. We are here to discuss the VOC, its impact on health, safety limits, and solutions to restrict the risks associated with VOCs.
What are VOCs?
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are a group of chemicals that highly vaporize into the air. Chemicals like benzene, ethylene glycol, methylene chloride, tetrachloroethylene, toluene, xylene, and 1,3-butadiene. These VOCs are themselves harmful, and some of them combine and form other pollutants as well.
Common products where VOCs are mostly present:
- Paints, paint strippers, and other solvents
- Wood preservatives
- Aerosol sprays
- Cleansers and disinfectants
- Moth repellents and air fresheners
- Stored fuels and automotive products
- Hobby supplies
- Dry-cleaned clothing
VOCs as pollutants:
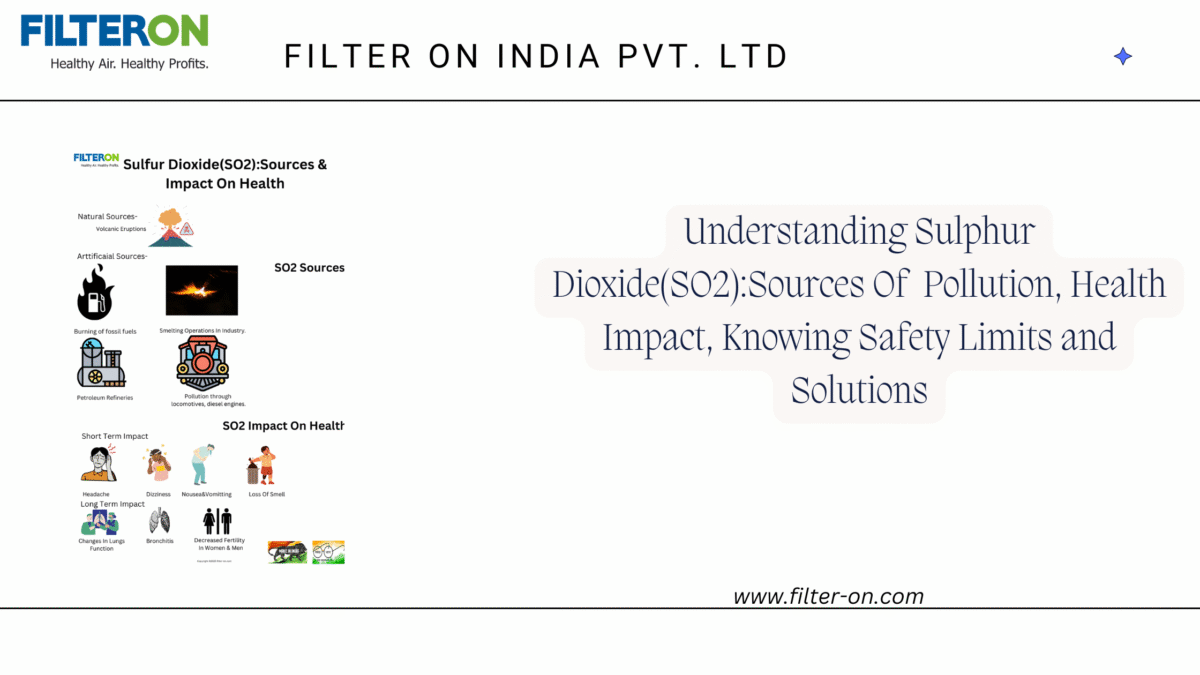
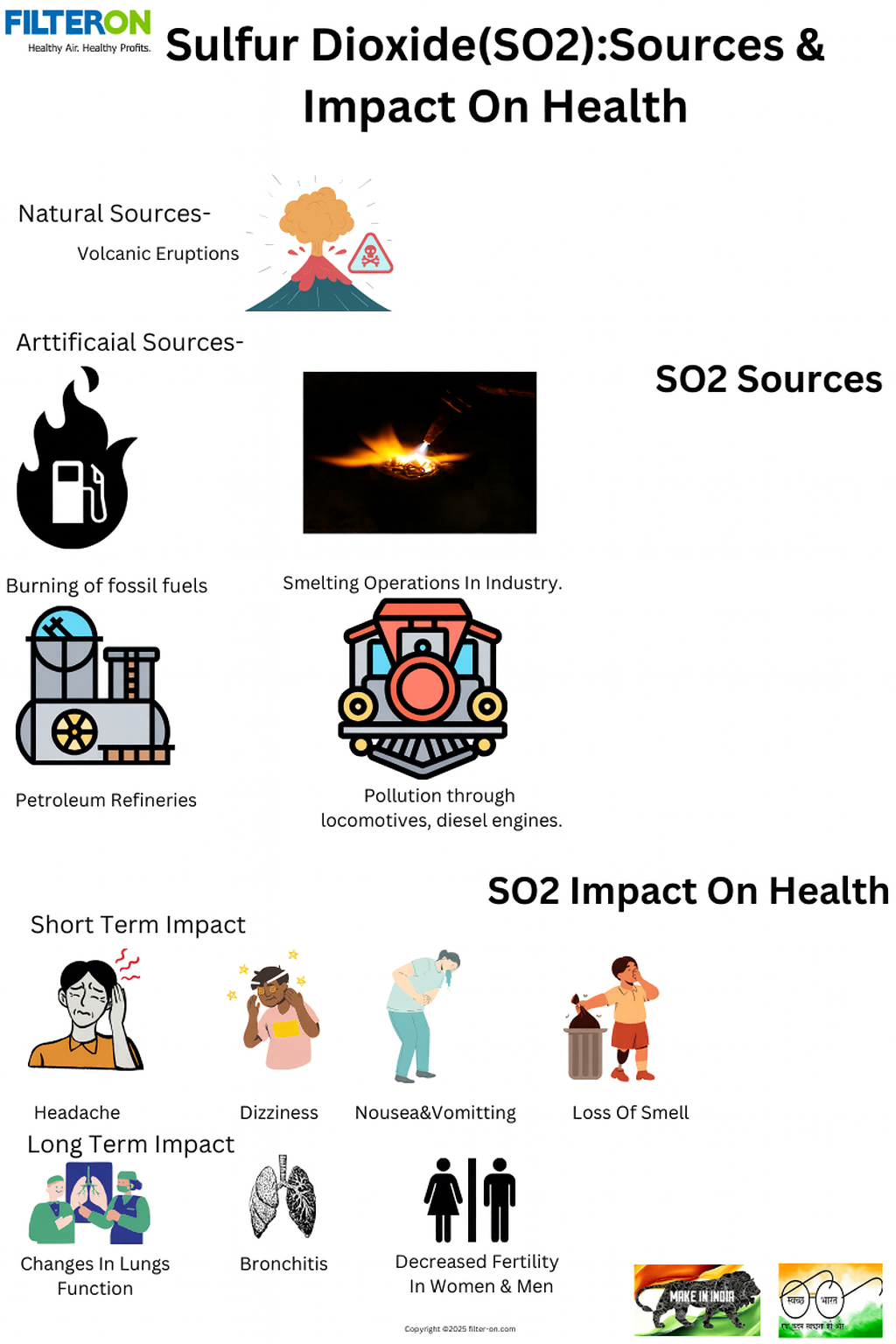
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are a group of pollutants that are responsible for air pollution. Some of the sources of VOCs are as follows:

Natural Sources-
Volatile organic compounds Natural sources are as follows:
- Plants: Many plants release harmful chemicals, and some can even absorb them.
- Forest fires: Natural forest fires are a source of VOCs.
- Anaerobic moors: Anaerobic moors processes are a source of VOCs.
- Cattle farms: Cow manure is a volatile source of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Anything burning: Anything that burns can be a source of VOCs.
Some of the other natural sources include volcanoes and fermentations.
Artificial Sources-
Artificial, man Made sources of VOCs include fuel production, distribution, and combustion, with the largest source being emissions from motor vehicles due to either evaporation or incomplete combustion of fuel and from biomass burning.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are industrial solvents, fuel oxygenates, and by-products from water treatment. They are often found in petroleum fuels, hydraulic fluids, paint thinners, and dry cleaning agents.
VOCs can come from industrial sources such as:
- Burning fossil fuels
- Power generation
- Manufacturing chemicals
- Crude oil processing
- Some metal production processes
Other sources of VOCs include:
- Gasoline, fuels, and solvents
- Paints, stains, strippers, and finishes
- Pesticides
- Personal care products
- Aerosol sprays
- Cleaners and room deodorizers
- New cabinets, furniture, and beds
- New carpets, rugs, and wood floors
According to Energy Education, a major contributor to VOCs is the evaporation of hydrocarbon-rich liquids. These include:
- Gasoline from car tanks or refueling stations
- Industrial solvents such as oil-based paint
- Barbecue starter fluid
- Cleaning products
Health Effects of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
The health effects of VOCs are as follows:
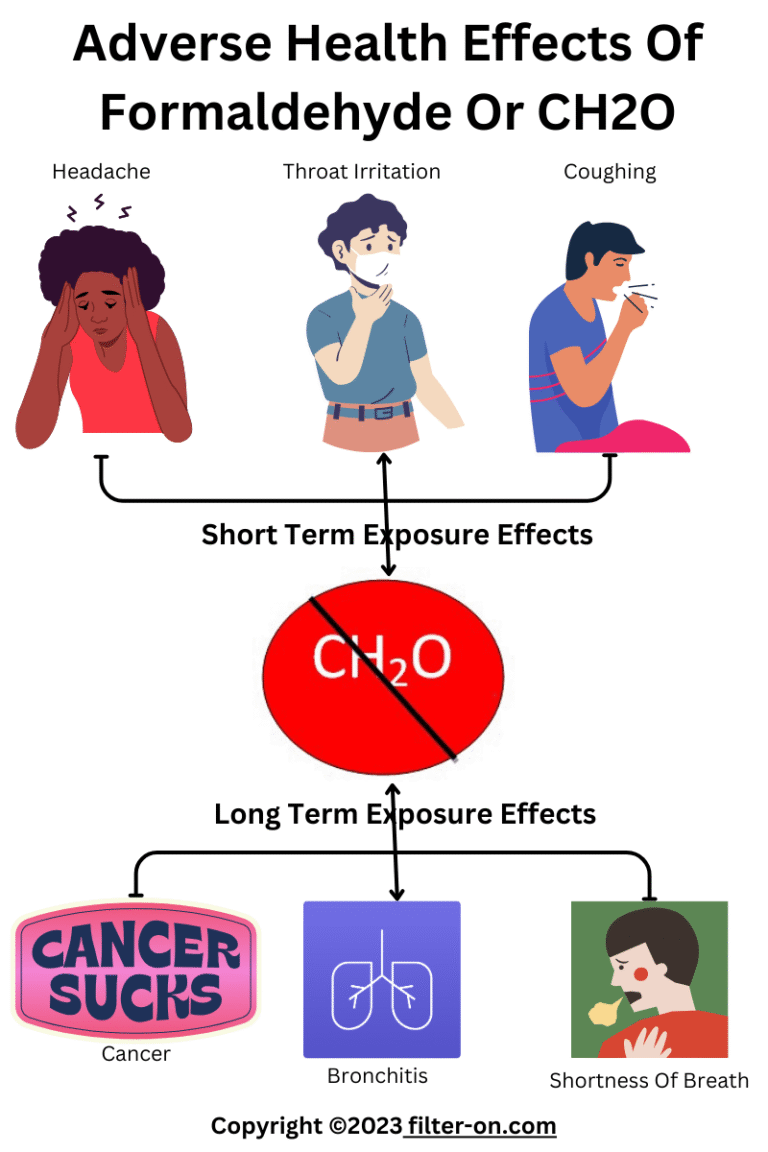
The health effects of VOCs on industrial workers and general people are categorized by short-term exposure and long-term exposure limits. Short-term exposure effects on health are immediate, and they have been for short periods of time, may be a few hours or a few days, whereas long-term health effects can be long-term exposure, may be a few years, to permanent effects on health. Both are categorized as under.
Short-term:
Short-term exposure to various VOCs may cause:
- Irritation of the eyes and respiratory tract
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Visual disorders
- Memory problems
Long-term:
Long-term exposure to various VOCs may cause:
- Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Loss of coordination
- Dizziness
- Damage to the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system
- Cancer
Industrial Safety Limits for VOCs
Safety Guidelines for Industries by CPCB With respect to VOC exposure
The industries can look more closely at the following aspects for the control of VOCs:
- Closed handling system for chemicals.
- Improved solvent recovery through the use of some special condensers and subcooling systems.
- Mechanical seal for chemical handling pumps.
- LDAR system – Venting of storages with trap receiver and condenser.
- Training for the laborers and staff.
- Proper system of loading and unloading of solvents.
- Proper solvent recovery systems.
- Work environment monitoring with respect to VOC has to be conducted and compared with the Factories Act’s occupational health standards.
- All the emissions emitting sources are to be channeled through ducts to a common conduit, and after advanced condensers and/or scrubbing with relevant or proper scrubbing, the treated emissions are to be let into the air.
Solutions for VOC exposure in industrial environments:
Solutions for VOC exposure in industries are as follows:
Proper Ventilation Measures:
Proper ventilation measures, such as LEV (local exhaust ventilation), must be installed in high-exposure areas of industries for worker safety.
Use of Extraction Systems:
Using extraction systems like Filter On India’s Clean Air Solutions in welding fumes solutions, oil mist extraction and dust collection solutions like welding fumes extractors, oil mist collectors, dust collectors, downdraft tables, and ESP filtration systems with HEPA must be used to control VOC exposure in industrial environments.
Follow guidelines set by authorities.
With regards to worker safety, industries must follow guidelines set by different authorities, such as OSHA, EPA, and CPCB, to control VOC exposure in industries.
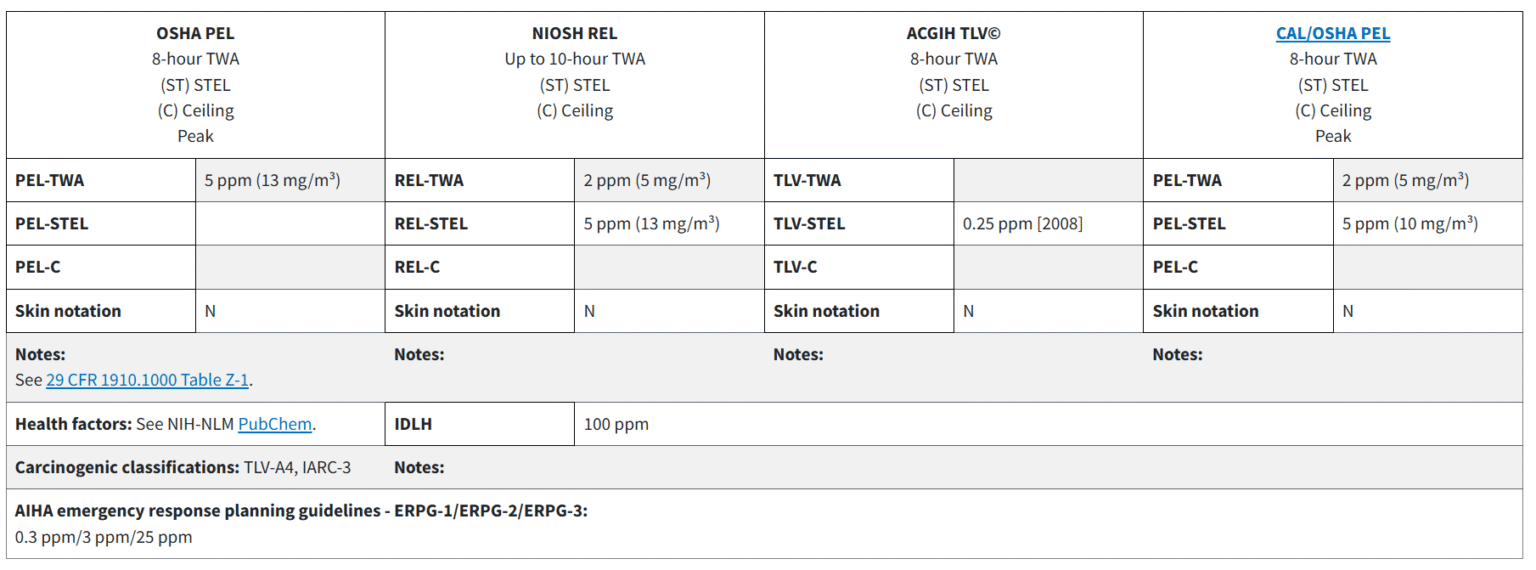
Industrial safety limits for VOCs are provided by OSHA,EPA, ACGIH, and in the Indian context, CPCB.
As per OSHA, ACGIH, and NIOSH, the permissible exposure limits for VOCs are as follows-
| Exposure Limits | |
| OSHA (PEL) | for general industry: 50 ppm (240 mg/m3) TWA; Skin for the Construction Industry: 50 ppm (240 mg/m2) TWA; Skin for Maritime: 50 ppm (240 mg/m2) TWA; Skin |
| ACGIH (TLV) | 20 ppm; Appendix A3: Confirmed Animal Carcinogens with Unknown Relevance to Humans |
| NIOSH (REL) | 5 ppm (24 mg/m2) TWA |
| NIOSH (IDHL) | 700 ppm |
The OSHA standards for VOCs can be read here.
Another example of regulations relating to VOC safety includes the EPA’s regulation 40 CFR 59. This federal regulation, “National Volatile Organic Compound Emission Standards for Consumer and Commercial Products,” targets overseas manufacturers and importers of certain products and seeks to ensure that such parties remain in compliance with VOC emission standards.
In the Indian context, the CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) has set the permissible exposure limits for pollutants, so for VOCs, its limits are as follows:
Moreover, there is no legislation for VOC in ambient air in India. As per the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) of India, benzene is the only VOC whose standard has been prescribed as 5 μg/m3 since November 2009.
Visit blogs to learn more about the critical features of clean air system design and air pollution control systems created by Filter On India.