Manual Welding Booth Fume Extraction: Choosing the Right Setup for Your Shop
Manual welding is an integral part of almost every manufacturing setup. Unlike robotic welding, which requires a higher investment and budget, manual welding is cost-effective and fits well within most operational budgets. That is why manual welding stations are present in nearly every manufacturing facility. However, an important question remains: what is the status of fume extraction at these manual welding stations?
Large organizations generally have the capability to install fume extraction systems for both manual and robotic welding stations unlike the small ones. In this article, we will cover Manual Welding Booth Fume Extraction in detail and discuss the right setup strategy for your welding shop.
Introduction to Manual Welding Fume Extraction
Manual welding includes various welding processes such as MIG welding, Stick welding, TIG welding, Plasma Arc welding, Electron Beam welding, and Laser welding. Each of these welding types generates fumes with different characteristics and therefore requires a suitable fume extraction system based on the welding process and several operational parameters. These parameters will be discussed one by one, starting with the potential dangers associated with manual welding.
Potential Dangers Due to Manual Welding
The risks associated with manual welding can be broadly categorized into immediate hazards and long-term health consequences, as outlined below.
Immediate Physical Dangers to workers:
- Risk of getting electric shock: One of the most serious and immediate risks. Contact with live components, such as the electrode holder, can result in severe injury or fatal electrocution, especially in damp or wet conditions.
- Skin burns: Welding temperatures can exceed 10,000°F, causing instant burns from arc contact, molten metal spatter, or hot workpieces.
- Fire and Explosions: Sparks and hot spatter can travel up to 35 feet, easily igniting flammable materials, gas cylinders, or residues inside used containers such as drums.
- Eye Injuries: “Arc eye” or welder’s flash is a painful corneal burn caused by ultraviolet radiation and can occur within seconds. Intense infrared radiation may also lead to immediate retinal damage.
Health Risks from Manual Welding Fumes
Manual welding produces a complex mixture of toxic metal particles and hazardous gases.
- Respiratory Illness: Short-term exposure can cause metal fume fever, throat irritation, and breathing discomfort. Long-term exposure is linked to lung cancer, kidney cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Neurological Damage: Inhalation of manganese fumes, commonly generated during mild steel welding, can cause irreversible nervous system damage and symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease.
- Suffocation: In confined spaces, shielding gases such as argon or helium can displace oxygen, leading to rapid unconsciousness or even death.
Long-Term Hazards
- Radiation Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation increases the risk of skin cancer and ocular melanoma.
- Hearing Loss: Noise from welding, grinding, and cutting operations often exceeds 85–100 decibels, which can result in permanent hearing damage over time.
- Muscle or Joint Pains: Repetitive movements and sustained awkward postures can lead to chronic back, shoulder, and neck pain.
2025 Safety Standards
- Mandatory Controls: Regulatory authorities such as HSE, CPCB, EPA, and OSHA state that welding operations should not be carried out without appropriate fume extraction or respiratory protection, regardless of job duration.
- Strict Exposure Limits: As of 2025, several regions have reduced workplace exposure limits for welding fumes, including aluminum fumes, to improve worker safety.

Manual Welding Fume Extraction: What It Is and How It Works
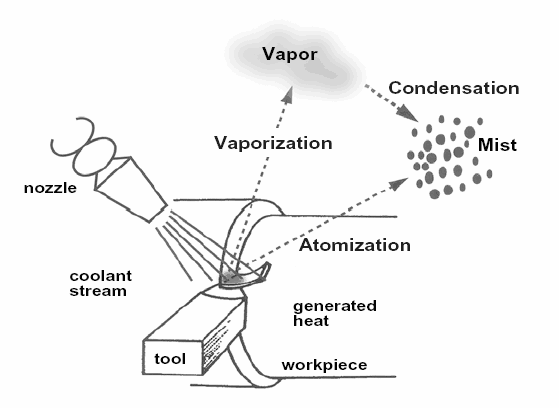
The working principle of a manual welding fume extraction system involves capturing fumes directly at the source. A hood is installed above or beside the welding station and connected to the fume extractor through ducting. Welding fumes are drawn through the hood and ducts into the filtration unit, where fine particulate matter is captured. Clean air is then discharged through the extractor fan back into the workplace or outside, depending on the system design.
A properly engineered fume extraction system is essential to capture hazardous fumes directly at the source before they disperse into the work environment.
Equipment such as a fume collector, fume extractor, or fumes extractor plays a key role in improving workplace safety and ensuring compliance with occupational health standards.
For applications involving gaseous pollutants, a fume scrubber system is commonly used to neutralize harmful vapors before air is released or recirculated.
Welding fume extraction solutions for Manual Welding Booths:
Welding operations generate toxic metal fumes that require effective source capture. A dedicated fume extractor for welding or fume extractor welding setup helps control exposure in manual and automated welding stations.
A complete welding fume extraction system or welding exhaust system is designed based on welding type, enclosure conditions, and duty cycle.
Proper welding fume exhaust not only improves air quality but also supports regulatory compliance, while system selection from certified welding fume extractor manufacturers ensures reliability and long-term performance.
The welding fume extractor price typically depends on airflow capacity, filtration efficiency, and system configuration.
Factors to Consider for Manual Welding Fume Extraction
When selecting a manual welding fume extraction system, several important factors must be considered.
- Number of Manual Welding Stations: The number of manual welding stations plays a key role in determining the size and capacity of the fume extraction system. It directly impacts the total airflow requirement and the coverage area of the system.
- Type of Welding & Manual welding fume extraction: Each welding process ARC, MIG, or TIG requires a fume extraction system designed according to its specific fume generation pattern and operational characteristics.
- Size of Welding Fixture or Table (L × W × H): The dimensions of the welding table or fixture are essential for calculating the required airflow capacity (CMH) of the fume extraction system.
- Enclosure Details: The level of enclosure around the welding booth whether fully enclosed, partially enclosed, or open directly affects fume capture efficiency and exposure levels.
- Material Handling System: The type of material handling system used, such as manual handling, automated systems, or EOT cranes, influences the placement and configuration of the fume extraction system.
- Welding Cycle Time:; The actual duration of welding operations determines overall fume exposure and helps define the required extraction capacity.
- Layout Availability: If a detailed layout is available, it becomes easier to plan optimal placement of the fume extractor and ducting. Proper layout planning ensures effective fume control without obstructing worker movement or compromising safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is fume extraction mandatory for manual welding?
Yes. Safety authorities such as OSHA, HSE, CPCB, and EPA mandate the use of appropriate fume extraction or respiratory controls during manual welding to reduce exposure to hazardous fumes and protect worker health.
Which fume extraction system is best for manual welding booths?
The ideal system depends on factors such as the welding process, number of welding stations, enclosure design, and airflow requirements. Common solutions include extraction arms, welding hoods, and downdraft tables that capture fumes directly at the source.
Are welding fumes harmful during short welding operations?
Yes. Even short-term exposure can cause metal fume fever, respiratory irritation, and eye discomfort. Repeated exposure without proper fume control can result in serious long-term health issues.
Can one fume extractor serve multiple manual welding stations?
Yes. A centralized fume extraction system can serve multiple manual welding stations if it is properly designed with adequate airflow capacity, balanced ducting, and effective fume capture at each station.
Visit blogs to learn more about the critical features of clean air system design and air pollution control systems created by Filter On India.